Dystonia Treatment in Mumbai
Dr. Gurneet Sawhney one of the best neurosurgeon in Mumbai provides the best treatment for dystonia.
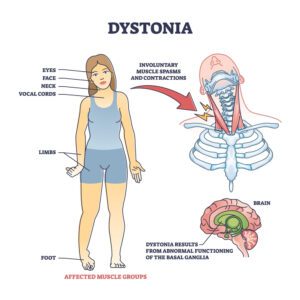
Dystonia is a very complex, highly variable neurological movement disorder that can affect young children and adults across the globe – irrespective of race, ethnicity, and other determining factors. Dystonia patients display involuntary muscle contractions such as repetitive movements, abnormal positions, and postures, uncontrollable twists. The organs affected could be the face, vocal cords, arms, legs, and trunk.
Causes of Dystonia
Dystonia results from abnormal functioning of the basal ganglia, a deep part of the brain which helps control the coordination of movement. These regions of the brain control the speed and fluidity of movement and prevent unwanted movements.
Dystonia may be inherited, acquired, or idiopathic (no known cause). Inherited disorders are transmitted genetically. In acquired forms, dystonia is caused by damage or degeneration of the brain (e.g. after a brain injury or stroke) or exposure to particular drugs. In idiopathic dystonia, there is no identifiable cause and no structural damage or degeneration to the brain.
Classification of Various Types of Dystonia
Dystonia is classified on the basis of age, symptoms displayed, the main cause and the affected body parts. Age plays a major role in the extent of the organs likely to be affected and its severity. This means that the earlier onset of dystonia will lead to its further spread across other organs of the body. If it occurs at a later stage, the symptoms will be moderate and restricted to a great extent.
Age-wise onset of dystonia:
0 – 12 years – Childhood onset
13 – 20 years – Adolescent onset
20 years and above – Adult onset
Classification of dystonia by body part
- Focal Dystonia: Focal dystonia affects people in the age group of 40s – 50s especially women and is also known as adult-onset dystonia. In most cases, focal dystonia is idiopathic i.e. no reason known, and is not genetic. Focal dystonia condition affects one area of the body viz.
- Neck – Cervical dystonia or spasmodic torticollis
- Eyes – Blepharospasm
- Lower face/mouth/jaw – Oromandibular dystonia
- Vocal cords – Laryngeal dystonia
- Upper or lower limbs – Limb dystonia
Some rare types of dystonias include - Trunk – Twisting, bending or unusual stretching of the truck
- Abdominal Wall – Writhing movements or sustained contractions of the abdominal wall.
- Segmental Dystonia: Patients with segmental dystonia have two or more parts of their body parts affected with dystonia. Generally, the second body part affected is located close to the primary site. It is observed that nearly 30% of focal dystonia patients could experience spasms in the areas located near their primarily affected site. For eg. dystonia conditions in the lower face along with symptoms in the jaw, mouth, and eyelids.
Other types of Segmental Dystonia are:
- Multifocal dystonia: Two or more body parts distantly located are affected
- Hemidystonia: Half of the body is affected; the legs are first affected followed by other regions in the body.
Cause wise classification of dystonia
- Idiopathic or Primary Dystonia: The neurosurgeon rules out secondary causes considering the presence of primary dystonias especially in children and adolescents which could be genetic in nature. Also, in cases of adult-onset of dystonia, the condition could be a variable one with either focal or segmental dystonia. Most of the early-onset cases of primary dystonia are caused by mutation of the DYT1 gene which is mapped to the long arm of chromosome 9 at 9q34.1. The main symptoms appear in the limb and spread across the body. Early-onset of primary dystonia has on onset age of 12 years on average while it is unlikely to develop after 29 years of age. DYT6 is yet another autosomal dominant primary dystonia. DYT6 is mapped to chromosome 8 (8p21q22). It is a rare condition and spreads to other organs of the body especially limbs, neck or head. The patient develops issues in speech articulating and difficulties. Other inherited primary dystonia conditions noted are DYT7, DYT2, and DYT4 especially those of European descent.
- Symptomatic or Secondary Dystonia: This dystonia occurs on account of secondary causes such as exposure to environmental hazards for eg. manganese or methanol, cyanide, carbon monoxide or presence of underlying health issues such as brain/spinal cord injuries, hypoparathyroidism or vascular malformations, cerebral palsy, brain tumors, Parkinson’s disease, inflammation in the brain, infections in the brains and certain medications.
- Dystonia-plus Syndromes: This condition results from neurological conditions along with neurodegenerative and neurochemical disorders. Some of these conditions are dopa-responsive dystonia (DRD) or Segawa syndrome, rapid-onset dystonia-parkinsonism (RDP) and myoclonus-dystonia.
- Heredodegenerative Dystonia: Heredodegenerative dystonia occurs if the patient is already suffering from inherited .neurological conditions leading to neurodegenerative disorders. These conditions include X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism (Lubag), Huntington’s disease, Wilson’s disease, neuroacanthocytosis, Rett’s syndrome, Parkinson’s disease and juvenile Parkinsonism, autosomal recessive and/or parkinsonian syndromes, X-linked recessive to name a few.
Symptoms of Dystonia
Diagnosing dystonia is quite complicated as its symptoms are similar to those of a stiff neck, stress or a psychological disorder. It is quite likely that treating doctors could diagnose the condition as a psychological disorder and other conditions while most of the symptoms being variable too.
Initial stage symptoms of dystonia:
- Most symptoms occur after certain tasks or movement
- They affect the same group of muscles or body i.e. a repetitive pattern
- The symptoms build gradually and stay localized suggesting a disorder
Dystonia initially arises after specific movements or tasks but, in advanced stages, it may occur at rest. It usually affects the same group of muscles, thus causing a repetitive pattern of movements over time. It generally develops gradually, with localized symptoms suggesting the presence of the disorder.
- Blepharospasm condition – Increased blinking, excessive sensitivity to bright light and eye irritation
- Oromandibular dystonia – Changes in speech cadence, difficulty chewing and subtle facial spasms
- Limb dystonia – fatigue during walking, or physical activity and cramps in the hand while writing
Stages of Progression in Dystonia
There are varying stages of progression in dystonia conditions. The rate of progression could steady or constant at a level usually at an early stage. In the progressive stage, the patient displays fast-paced involuntary movements in a particular rhythm, abnormal gait, contortions of the torso and twisting postures which leaves the patient with fixed deformities of the posture.
The patient may not always complain of pain but there could be discomfort in the affected area. In the long run limb dystonia patients could complain of uncontrolled muscle movement leading to pain and degeneration of joint and arthritis condition while cervical dystonia patients are likely to complain of headaches, irritation of nerve roots, and so on.
Diagnosis and Treatment
It is quite difficult to diagnose the onset of dystonia at an early stage. However, it is advisable to visit a doctor if the patient complains of involuntary muscular contractions.
Don’t let Dystonia hold you back. Start your journey towards relief
When & How to Seek Medical Care
Early signs of dystonia often are mild, infrequent and linked to a specific activity. See your doctor if you are experiencing involuntary muscle contractions. With no specific tests to rely on, most experienced neurosurgeons in India suggests a brain MRI to rule out other conditions. In case of a family member being affected with the same, genetic testing is advised.
Treatment
The treatment focuses on relieving the patient from pain and discomfort associated with dystonia. Dr. Gurneet Sawhney would suggest –
- Botulinum toxin – Botox injections
- Special Medication
Surgery
These approaches could be used as a stand-alone treatment or in a combination with the intention to block the communication between the muscles and the nerves that cause abnormal postures and movements.
Deep brain stimulation (DBS), stereotactic thalamotomy, pallidotomy, and cervical rhizotomy and other surgeries are suggested only if medication and other treatments do not provide relief and affect the quality of life of the patient.
In deep brain stimulation surgery, the neurosurgeon inserts a battery-powered stimulator in the body to deliver an electrical stimulation to that area of the brain which causes these painful dystonia symptoms. The intensity of the stimulation is controlled though a remote control device. Surgeries such as stereotactic thalamotomy, pallidotomy, and cervical rhizotomy are preferred as they are less risky with minimal side effects and better outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does dystonia affect bone health?
No, not directly, however the bones may experience stress and pressure on account of abnormal postures and spasms. It is likely that the ligaments and tendons get shortened or contracted and the patient experience a limited range of motion. Also, the posture of the important bones and the patient’s overall posture can undergo a major change that requires further management and treatment.
Can dystonia lead to death?
No, it can lead to the development of life-threatening conditions which are uncommon and treatable too. But dystonia does not make the lives of the patients shorter but at times multiple body areas are affected leading to complications which can be managed by prompt treatment.
At what rate does dystonia occur? Is it possible to identify the early signs or symptoms of dystonia?
Generally, the onset of dystonia is at a gradual pace. Early signs of dystonia are mild and subtle, also these symptoms are associated with the affected body parts. For instance, a change in the pitch of the speech could indicate laryngeal dystonia while spasms in the jaw indicate jaw dystonia and so on. However, rapid-onset dystonia-parkinsonism and acute dystonic reactions can appear within days or hours. Acute dystonic reactions is associated with antipsychotic drugs
How does the neurosurgeon diagnose dystonia condition in a patient?
An expert neurosurgeon will seek in-depth patient history, conduct detailed investigations and tests to ascertain the dystonia condition. Very often, it is possible to identify the condition but knowing the cause is uncertain.
Blogs
How Does the Brain Recover After a Seizure?
Nobody talks about what happens after the seizure stops. Everyone focuses on the episode itself. Timing it. Getting the person safe. Calling for help. But the recovery that follows, that part carries just as much clinical weight. Sometimes more. The brain doesn't...
How To Book an Online Consultation with Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawhney?
You don't need to travel to Mumbai for a proper neurosurgical opinion. Booking an online consultation with Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawhney is straightforward. Call, WhatsApp, or email the clinic, share your scans beforehand, and you'll get a confirmed slot within 24 to 48...
Who Is the Best Neurosurgeon for DBS Surgery in Mumbai?
Looking for the best neurosurgeon in Mumbai for DBS surgery? Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawhney at Fortis Hospital explains who needs it and what real results look like.