Being detected with carotid artery disease can be disturbing. Don’t worry; conservative and surgical options are available to treat this condition. But choosing a suitable treatment option can be challenging.
Dr. Gurneet Sawhney, a highly qualified and experienced neurosurgeon in Mumbai, says, “many patients’ first thought, when diagnosed with carotid artery disease, is, ‘Oh my god, I need surgery to fix this right away. “However, it’s critical to be aware of your options and to proceed cautiously.”
Dr. Sawhney advises patients to seek a second opinion before undergoing surgery for carotid artery disease, especially if they have not had a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
Moreover, Dr. Sawhney specializes in determining the best procedures and approaches for even the most complex cases. “Treating carotid artery disease entails more than just executing a surgical procedure; we consider all options,” says Dr. Sawhney.
In this article, we will discuss more about carotid artery disease and its treatment options.
What is carotid artery disease, and how does it affect you?
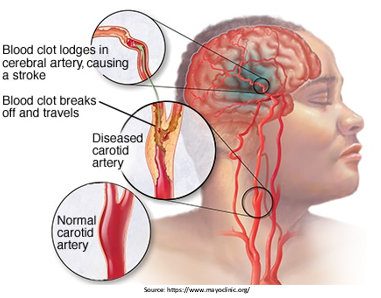
A carotid artery is the blood vessel that circulates blood to the brain. When these get clogged with plaque, carotid artery disease occurs. Plaques are clumps of lipids, cholesterol, calcium, and other chemicals that block the arteries.
Carotid artery disease can limit oxygen delivery to the brain since the carotid arteries convey blood to the brain. A stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) can develop when the narrowing of the carotid arteries is severe enough to stop blood flow.
Similarly, if bits of plaque break off and enter to the brain, they can cause a stroke or a transient ischemic attack (TIA).
What are the risk factors for carotid artery disease?
- Atherosclerosis, which occurs when plaque builds up and narrows your arteries, is the most common cause of carotid artery disease. Hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease are linked to atherosclerosis.
- A family history of carotid artery disease, age, and genetics are risk factors and plaque build-up in the arteries.
- Other health issues and activities, such as alcohol consumption, smoking, obesity, and high cholesterol, can raise your risk of developing carotid artery disease.
What are the signs and symptoms of carotid artery disease?
- According to Dr. Gurneet Sawhney, one of the best neurosurgeon in India, carotid artery disease can be asymptomatic or symptomatic.
- “Many people with carotid artery disease don’t have symptoms until the condition has progressed to the point where it causes a TIA or stroke,” explains Dr. Gurneet.
- “Vision issues, slurred or garbled speech, a one-sided facial droop, and a weakness in or inability to move limbs” are among the symptoms.
- TIA symptoms are usually transient, lasting from a few minutes to a few hours. Because TIAs are significant indicators of future stroke, they should be handled as severe medical emergencies requiring immediate medical attention.
- If you don’t have any symptoms but have risk factors for carotid artery disease, your doctor may order an ultrasound or other imaging examination of your carotid arteries.
- These tests help the doctor evaluate how severe your condition is and if your carotid arteries have a dangerous amount of obstruction.
Is surgery considered necessary for carotid artery disease?
- To treat patients with carotid artery disease, Dr. Gurneet Sawhney, a seasoned brain doctor in Mulund, Mumbai, collaborates with a multidisciplinary team of vascular surgeons and interventionists.
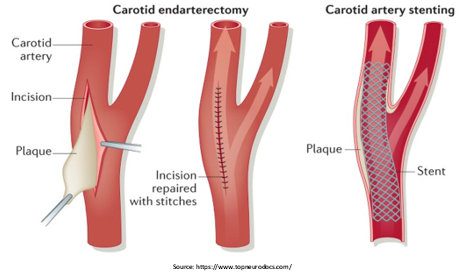
- If you have had a TIA or stroke or your carotid artery is severely clogged, surgery to remove the plaque may be beneficial. The procedure is known as carotid endarterectomy. This surgery is time-sensitive, and it should be performed as soon as possible after a stroke or TIA to avoid a second stroke.
- The surgeon creates an incision in the neck just below the jaw during this procedure. Then, the surgeon opens the carotid artery and gently eliminates the plaque. The surgeon then stitches the incision and seals the artery with a patch.
- When the surgeon considers a patient with carotid artery disease at too high risk for carotid endarterectomy or if they have had previous neck surgery or radiotherapy, they may recommend endovascular repair, commonly known as carotid artery stenting.
- Carotid artery stenting is a minimally invasive procedure. It involves inserting a balloon-tipped catheter through a small incision. The catheter is carefully directed to the blockage in the carotid artery. The surgeon inflates the balloon tip that compresses the plaque against the blood vessel wall. Then, the surgeon permanently implants a tiny metal device or stent shaped to strengthen the artery and maintain blood flow.
Let’s know the Benefits and Risks of Endovascular Carotid Artery Stenting
Your doctor may discuss the risks and advantages of the procedure. The risks may vary depending on the severity of the condition, the location of the blockage, whether you have had a previous stroke, and the existence of other medical conditions.
Benefits
- Safe and less-invasive procedure.
- No need for hospitalization.
- Faster recovery with less pain.
- Better and accurate results.
- Low risk of infection and other complications.
Risks or Complications
- Bleeding or Bruising at the catheter insertion site.
- Damage to arteries.
- Stroke.
- There could be other potential risks. Please ask questions at your consultation with your doctor to fully understand why the procedure is being recommended and the risks involved.
- However, surgery may not be the best treatment option if you have no symptoms of carotid artery disease.
- According to research, people with asymptomatic carotid artery disease have a lower risk of stroke. We can help these patients maintain their condition without surgery in many cases.
- Several studies suggest that surgical intervention is less necessary than appropriate medicinal therapy in managing carotid artery disease. For many people, the optimal treatment for carotid artery disease is a combination of lifestyle changes and drugs.
- This is especially true for people who might find surgery difficult and risky, such as those who have had past neck surgery, radiation, or cardiac problems.
- Dr. Sawhney advises that any patient who has had a stroke, mini-stroke, or TIA should be checked for carotid artery disease, generally done with a simple, short ultrasound examination.
- Carotid endarterectomy or carotid stenting effectively reduces the likelihood of another or more catastrophic stroke if the carotid artery is narrowed.
Why is it important to get a second opinion on carotid artery surgery?
Dr. Gurneet Sawhney explains, “Because we give specific treatments customized to each patient’s condition, having a second opinion from a specialist ensures you are getting the finest care for your carotid artery disease.”
Having a second opinion can be highly beneficial if:
- You have a complicated surgical situation.
- You are worried about picking the appropriate treatment.
- Other health issues make surgery riskier.
- You have been advised that your condition is either incurable or untreatable.
If you notice any signs or symptoms of a stroke, seek medical help right away. You may have suffered TIA, which is an indicator of stroke. Even if they last a few minutes, and then you feel fine, you should visit a doctor immediately.
Consult your doctor if you have risk factors for carotid artery disease. Even if you don’t experience any symptoms, your doctor may recommend intensive treatment to keep you from having a stroke.
Seeing a doctor early enhances your chances of having carotid artery disease detected and treated before suffering a severe stroke.
