A subdural hematoma (SDH) is a collection of blood between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater, two of the protective membranes covering the brain. This condition often arises from head injuries that cause veins to tear, leading to blood accumulation in the subdural space. Globally, SDHs are a significant concern, especially among the elderly and those on anticoagulant therapy. In India, with its vast population, the incidence of SDHs is notable, particularly due to road traffic accidents and falls.
Dr. Gurneet Sawhney, an acclaimed neurosurgeon in Mumbai, states:
“Subdural hematomas can sometimes present symptoms weeks or even months after the initial injury. Factors such as minor head traumas, especially in individuals on blood thinners, or in the elderly with brain atrophy, can lead to delayed onset of symptoms. Monitoring neurological changes is crucial even long after a seemingly insignificant head injury.”
This article delves into the occurrence of subdural hematomas two months post-injury. Let’s explore the associated symptoms, available treatment options, and the recovery and rehabilitation process.
Symptoms of Subdural Hematoma After 2 Months
Subdural hematomas can manifest symptoms long after the initial injury, making them particularly stealthy. Two months post-injury, individuals might experience:
- Persistent or worsening headache that doesn’t respond to typical pain relievers
- Cognitive impairments, including difficulties with memory, concentration, or decision-making

- Motor deficits, such as weakness or numbness in limbs, often on one side of the body
- Speech difficulties, including slurred speech or trouble finding the right words
- Visual disturbances causing blurred or double vision
- New-onset seizures without a prior history
These symptoms arise due to the gradual accumulation of blood, which increases pressure on the brain tissues, leading to neurological deficits.
Are you or a loved one experiencing persistent headaches or cognitive changes after a head injury? It’s essential to consult a proficient neurosurgeon for a thorough evaluation.
But what can be done if these symptoms arise? Let’s explore the treatment options available.
Treatment Options for Subdural Hematoma 2 Months Later
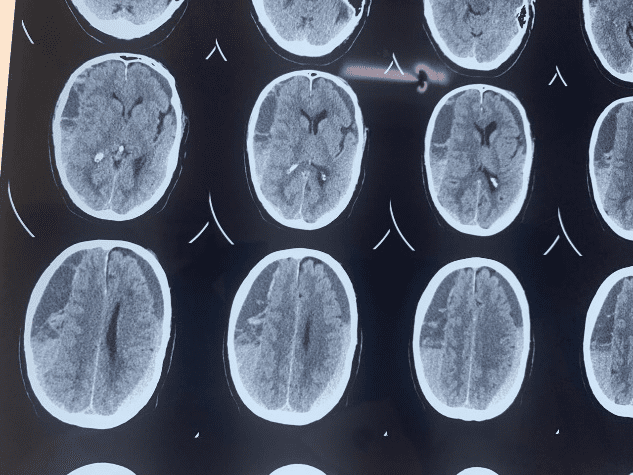
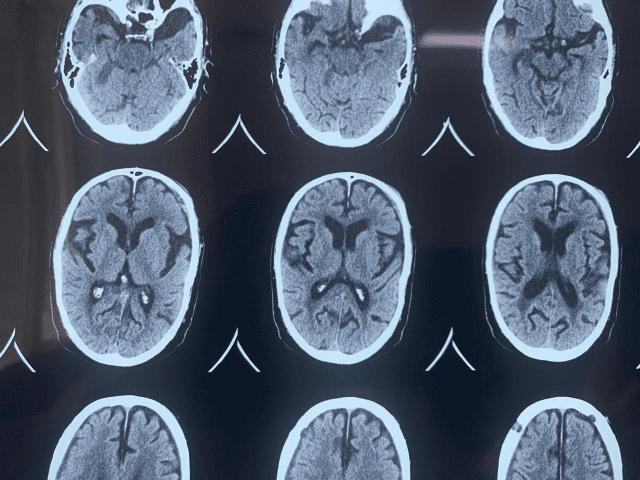
Addressing a subdural hematoma two months after injury requires a comprehensive approach:
Case of bilateral Subdural Hematoma (SDH) – Before and After
Imaging Studies:
Initial assessment involves CT or MRI scans to determine the hematoma’s size, location, and whether it is stable or growing. These imaging tests help doctors decide the most appropriate course of action.
Conservative Management:
Close monitoring with regular imaging may be sufficient for small, asymptomatic hematomas. Patients should avoid blood-thinning medications and high-impact activities that could worsen the condition.
Medication:
In cases of inflammation, corticosteroids might be prescribed to reduce swelling. Your doctor may also give antiepileptic drugs to prevent seizures, which can occur in some patients with brain injuries.
 Blood Pressure Management:
Blood Pressure Management:
Controlling high blood pressure is essential to prevent further bleeding and reduce the risk of hematoma expansion. Doctors may prescribe antihypertensive medications and recommend lifestyle modifications.
Surgical Intervention:
If the hematoma exerts significant pressure or causes pronounced symptoms, procedures like burr hole drainage or craniotomy may be necessary to evacuate the blood. In some cases, the surgeon may use a minimally invasive endoscopic approach to reduce recovery time.
Dr. Sawhney, a renowned brain tumor surgeon in Mumbai, emphasizes:
“The choice between conservative and surgical management depends on factors like the patient’s age, overall health, and the hematoma’s characteristics. Timely intervention can significantly influence outcomes. Early detection, ongoing monitoring, and individualized treatment plans are crucial in ensuring a smoother recovery.”
Wondering about the road to recovery after treatment? Let’s delve into the rehabilitation process.
Recovery & Rehabilitation After Subdural Hematoma
Recovery from a subdural hematoma varies based on the severity and treatment approach:
Immediate Post-Treatment:
Patients may experience fatigue, mild cognitive challenges, and temporary balance issues, requiring close medical supervision.
Weeks 1-4:
Engagement in physical therapy to restore motor functions and occupational therapy to regain daily living skills. Cognitive exercises may be introduced to strengthen memory and problem-solving abilities.
Bilateral Subdural Hematoma Case – 93 Years Old Happy And Heathy Patient
Months 2-3:
Continued cognitive rehabilitation to address memory or attention deficits. Patients may also undergo speech therapy if communication difficulties persist.
Lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet and structured sleep patterns, aid in long-term recovery.
Beyond 3 Months:
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers to monitor progress and address any lingering issues. Some individuals may require ongoing rehabilitation for several months, depending on their neurological function.
Dr. Sawhney, a trusted doctor for Trigeminal Neuralgia Treatment in Mumbai, advises:
“Patience and persistence are key during rehabilitation. Each individual’s recovery journey is unique, and a tailored approach ensures the best outcomes. A multidisciplinary team, including neurologists, physiotherapists, and psychologists, plays a vital role in helping patients regain independence and quality of life.”
Noticing lingering symptoms after a head injury? It’s imperative to consult a knowledgeable neurosurgeon for an assessment.
Conclusion
In summary, subdural hematomas can present delayed symptoms, underscoring the importance of vigilance after head injuries. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for optimal recovery.
Dr. Sawhney, a seasoned brain and spine surgeon in India, offers reassurance:
“With advancements in medical imaging and treatment modalities, many patients with subdural hematomas can achieve full recovery. Early consultation with a neurosurgeon can make all the difference.”
Still have questions? Let’s address some common concerns about subdural hematomas.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Can a subdural hematoma resolve on its own?
Small, asymptomatic subdural hematomas can sometimes be reabsorbed by the body over time. However, regular monitoring is essential to ensure they don’t enlarge or cause symptoms.
2. What are the risks of delaying treatment for a subdural hematoma?
Delaying treatment can lead to increased pressure on the brain, resulting in permanent neurological deficits or even death. Timely medical intervention is crucial.
3. What lifestyle changes are recommended after recovering from a subdural hematoma?
Patients are advised to avoid activities that may lead to head trauma, such as contact sports. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper management of blood pressure and medications (especially blood thinners) can help prevent recurrence.
4. Is it safe to fly after experiencing a subdural hematoma?
In most cases, flying is not recommended immediately after a subdural hematoma, especially if symptoms persist or if surgery was performed. Consulting a neurosurgeon before travel is crucial to ensure safety.
5. Can a subdural hematoma reoccur?
Yes, there is a possibility of recurrence, especially in elderly individuals, those with coagulation disorders, or patients who have undergone surgical drainage. Regular follow-ups and imaging tests can help detect any reaccumulation of blood.
6. How long does it take to return to normal activities after treatment?
Recovery varies based on the severity of the hematoma and the type of treatment received. Some patients return to light activities within a few weeks, while others may need months of rehabilitation before resuming normal daily functions.
Are you concerned about symptoms persisting after a head injury? Seek guidance from an experienced neurosurgeon to ensure timely and effective care.
Reference Links:
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1137207-treatment
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21183-subdural-hematoma
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only and not for promotional use.

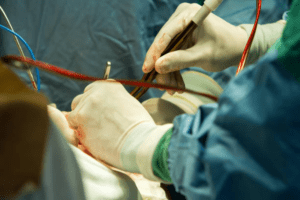 Blood Pressure Management:
Blood Pressure Management: