A tumor on left frontal lobe can cause a range of challenges and symptoms, affecting both physical and cognitive functions. This part of the brain is crucial for decision-making, problem-solving, and controlling movement. Tumors in this area can result in various issues, from personality changes to motor skill difficulties. This type of tumor accounts for approximately 10-15% of brain tumor cases worldwide, with a significant percentage occurring in India.
“Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for effective treatment,” emphasizes Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawney, one of the best neurosurgeon in Mumbai. He highlights the importance of timely intervention, stating that “Understanding the nature of the tumor and taking prompt action can significantly improve treatment outcomes and patient’s quality of life.”
With over 18 years of experience, Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawhney is renowned for his expertise in complex brain surgeries, including frontal lobe tumors. His proficiency in conventional and minimally invasive neurosurgery, combined with a patient-centric approach, makes him a sought-after specialist for those seeking effective brain tumor treatment in Mumbai.
What Type of Tumors are Usually on the Frontal Lobe?
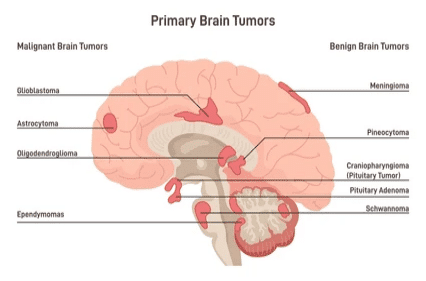 The frontal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the brain. It is susceptible to various types of tumors, including benign and malignant ones. The most common types of tumors affecting the frontal lobe are meningiomas, gliomas, and glioblastoma multiforme (GBM).
The frontal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the brain. It is susceptible to various types of tumors, including benign and malignant ones. The most common types of tumors affecting the frontal lobe are meningiomas, gliomas, and glioblastoma multiforme (GBM).
Meningiomas are typically non-cancerous. They can cause neurological symptoms by exerting pressure on surrounding tissues. Gliomas originate from glial cells and can vary in growth speed from slow to aggressive.
Glioblastoma multiforme is the most severe type of brain tumor in the frontal lobe. It is highly aggressive, grows rapidly, and can invade nearby brain tissue, making it challenging to treat. Due to its impact on the brain lobes, this type of tumor often presents severe symptoms. Glioblastoma usually doesn’t spread to other body parts but can significantly affect brain function due to its invasive nature.
Early detection and accurate classification of the tumor type are essential for determining the treatment strategy. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention can make a significant difference in effectively managing a frontal lobe tumor.
Frontal Lobe Brain Tumor Symptoms
If you have a tumor in the left frontal lobe, you may experience various symptoms that can impact your daily life. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
- Persistent headaches, especially in the morning or when lying down
- Changes in personality or behaviour, such as increased irritability or depression
- Difficulty with concentration, planning, and decision-making
- Memory loss and confusion
- Impaired motor skills, such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Seizures or sudden episodes of altered consciousness
- Vision problems, including blurred or double vision
- Speech difficulties, such as slurred speech or trouble finding words
Don’t wait for symptoms to worsen. Consult a specialist for a thorough diagnosis and treatment plan.
How Are Tumors on the Left Frontal Lobe Detected?
- Neurological Examination
Your doctor will assess your vision, balance, reflexes, and cognitive skills. This helps identify any signs that might point toward a frontal lobe tumor.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
An MRI scan creates detailed images of your brain. It helps locate the exact position and size of the tumor.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
A CT scan provides a comprehensive view of the brain. It highlights abnormalities that may not be visible in an MRI, especially when quick evaluation is needed.
- PET Scan (Positron Emission Tomography)
This imaging test helps determine the tumor’s activity level by detecting abnormal cell growth. It provides insight into whether the tumor is benign or malignant.
- Biopsy
Sometimes, a biopsy is performed to remove a small tissue sample from the tumor. It’s the most definitive way to understand the tumor’s type and guide treatment.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
EEG monitors brain activity to detect abnormal patterns that might be caused by a tumor. It’s particularly beneficial if a patient experiences seizures or other neurological symptoms.
Each test is crucial in confirming the diagnosis and forming a clear picture of your condition. Early and accurate detection helps plan the most effective treatment.
Treatment Strategies for Tumors on the Left Frontal Lobe
When dealing with tumors on the left frontal lobe, treatment depends on whether the tumor is malignant (cancerous) or benign (non-cancerous). Some of the effective treatment options include:
- Surgical Removal
Surgery is often the first step in treating both malignant and benign tumors. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without causing damage to healthy brain tissue. Surgical treatment of frontal lobe tumors requires careful planning and expertise.
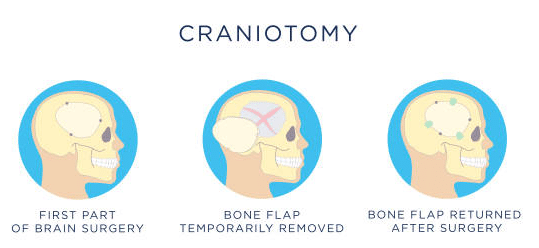
This is the most common surgical approach for both malignant and benign tumors. In this procedure, the surgeon temporarily removes the section of the skull to access the brain. Then, they carefully remove the tumor, aiming to preserve healthy brain tissue.
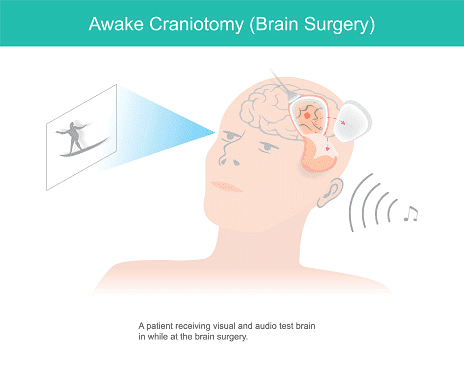
- Awake Brain Surgery
Also known as an awake craniotomy, this surgical procedure is performed for tumors located near critical brain areas that control speech, movement, or other essential functions. The patient remains awake during the surgery, allowing the surgeon to monitor brain activity in real-time. This method ensures the tumor is removed with minimal impact on vital brain functions.
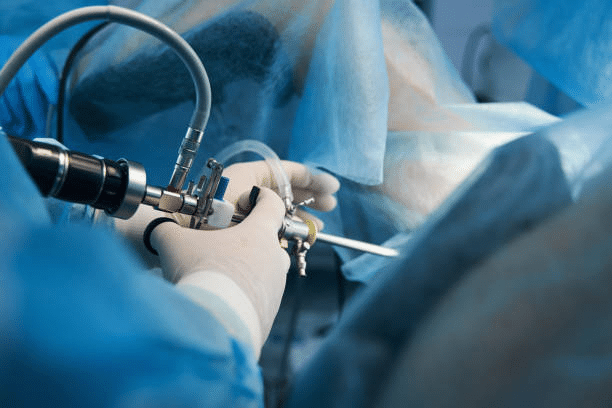
- Minimally Invasive Endoscopic Surgery
This surgery is especially beneficial for smaller or accessible tumors. Using a tiny camera and specialized instruments, the surgeon makes small incisions to remove the tumor. Compared to traditional open surgery, this approach reduces recovery time, minimizes scarring, and decreases the risk of complications.
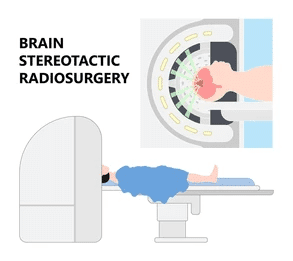
- Stereotactic Surgery
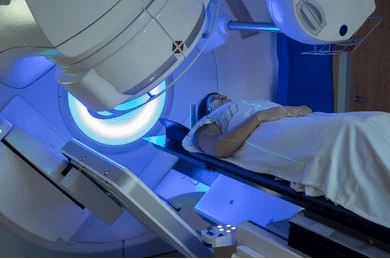
- Radiation Therapy
It involves high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It’s commonly used after surgery to kill any remaining malignant cells or as the primary treatment when surgery isn’t an option. It may also be used for benign tumors if the tumor grows or causes symptoms.
- Chemotherapy
It uses drugs that kill or slow the growth of cancer cells. Chemotherapy is often used for malignant tumors and can be administered orally or through an IV. It’s typically used alongside radiation for a more comprehensive approach.
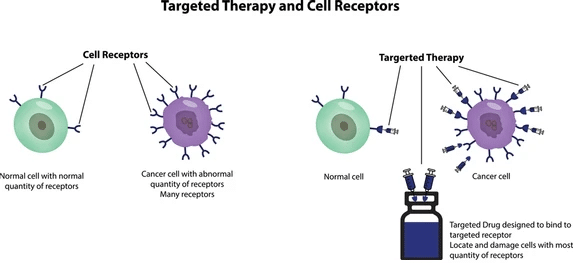
- Targeted Therapy
This therapy involves drugs that specifically attack cancer cells without harming normal cells. They target specific genes or proteins involved in tumor growth, offering a more personalized treatment.
Combined or individually, these treatments are tailored based on the type, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health and symptoms.
Conclusion
Tumor on left frontal lobe present unique challenges due to their impact on critical brain functions. Accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan are essential for effective management.
Consulting with a specialist like Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawhney, a prominent neurosurgeon in Mumbai, can help you understand your condition better and outline a customized treatment plan. From advanced surgical options to targeted therapies, you have choices that can lead to better management and recovery.
Don’t wait for symptoms to worsen. Consult a specialist for a thorough diagnosis and treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- How serious is a frontal lobe tumor?
A frontal lobe tumor can be severe, affecting cognitive functions, behaviour, and movement. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
- How much is the frontal lobe brain tumor life expectancy?
Life expectancy varies depending on the type, size, and stage of the tumor. With timely treatment, many patients, especially with low-grade tumors, live several years or longer.
- What is the left frontal lobe tumor prognosis?
The prognosis depends on factors like tumor type and location. However, early intervention often leads to better outcomes. Regular monitoring is crucial.
- How long does it take to recover from frontal lobe tumor surgery?
Recovery times vary; most patients need several weeks to months for full recovery. It depends on individual health and treatment response.
- Can a frontal lobe tumor recur after treatment?
There is a possibility of recurrence, particularly with aggressive types. Regular follow-ups and monitoring are essential.
Reference links:
https://academic.oup.com/brain/article/137/9/2532/2848278
https://www.moffitt.org/cancers/brain-tumor/location/
Disclaimer: This page provides general information about the tumor on left frontal lobe and does not aim to advertise or promote medical services or practitioners.