When the blood stops flowing to a part in the brain, the corresponding body part stops responding. This is known as a stroke. This blood supply loss can be ischemic (lack of blood flow) or haemorrhagic (bleeding into brain tissue).
Because strokes are life-threatening or may cause lifelong disability, they are considered a medical emergency. Ischemic strokes can be treated, but only if treated during the first few hours after the symptoms of a stroke appear.
Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawhney, one of the top neurosurgeons in India, has 14+ years of experience and has a strong base in Functional Neurosurgery, Epilepsy Surgery, managing Neurotrauma, Neurooncology, Neuroendoscopy procedures.
He specializes in many more procedures related to the brain and spine. You can consult DR. Gurneet Singh Sawhney if any of the symptoms appear.
Symptoms of Stroke:
If you observe any signs or symptoms of a stroke, seek medical help immediately, even if they seem to come and go or entirely disappear. Do the following in a “FAST” manner:
- Headache, dizziness, blurred vision
- Trouble communicating
- Trouble walking
- Face. Is your face drooping on one side when you smile?
- Arms. If there is difficulty in lifting both arms properly and equally.
- Speech. If the speech is slurred.
- Time. If you see any of these symptoms, seek emergency medical assistance right away with one of the best neurosurgeons in Mumbai.
Causes of Stroke
A blocked artery (ischemic stroke) or a leaking or bursting blood vessel are the two most common causes of stroke (haemorrhagic stroke). A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a momentary disruption of blood flow to the brain that does not cause permanent symptoms in some persons.
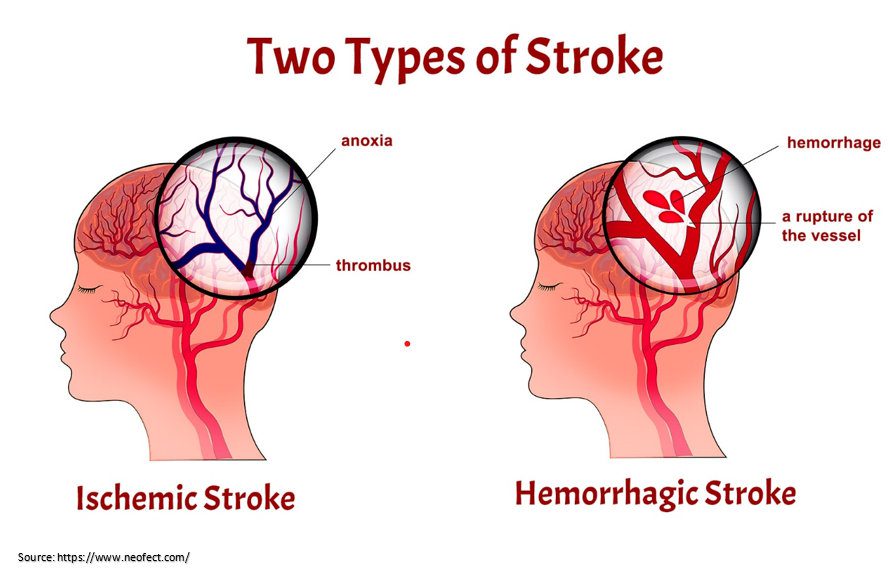
Ischemic stroke
It is the most common. It occurs when the blood arteries in the brain narrow or block, resulting in substantially restricted blood flow (ischemia). Fatty deposits that build up in blood vessels, as well as blood clots or other debris that move through your bloodstream and lodge in the blood vessels in your brain, produce blocked or restricted blood vessels.
Stroke due to haemorrhage
When a blood vessel in your brain leaks or ruptures, it causes a haemorrhagic stroke. Many disorders that alter your blood arteries might cause brain haemorrhage. Haemorrhagic stroke is caused by several factors, including:
- High blood pressure
- Excessive use of blood thinners (anticoagulants)
- Bulges at weak places in the walls of your blood vessels (aneurysms)
- A traumatic event (such as a car accident)
- Protein deposits in the walls of blood vessels cause vessel wall weakening (cerebral amyloid angiopathy)
- Haemorrhage as a result of an ischemic stroke
- The rupture of an aberrant tangle of thin-walled blood arteries is a less common cause of brain bleeding (arteriovenous malformation).
Ischemic attack with a transient onset (TIA)
A transient ischemic attack TIA happens when a clot or debris prevents blood flow to a region of your neurological system for a very short time. The symptoms are similar to an ischemic stroke but disappear shortly.
You may have a narrowed artery or partly blocked artery leading to your brain if you have experienced a TIA. If you have a TIA, you are more likely to have an Ischemic stroke later. So, please consult your doctor immediately.
Risk factors
Your stroke risk might be increased by a variety of circumstances. The following are some of the potentially treated stroke risk factors:
- Obesity or being overweight
- Inactivity on the physical level
- Binge or heavy drinking
- Cocaine and methamphetamine use are examples of illegal substances that are a potential risk.
- Medical conditions that are a potential risk
- High Blood Pressure
- Secondhand smoke exposure or cigarette smoking
- Cholesterol levels are high.
- Diabetes
- Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
- Heart Diseases
- Stroke, heart attack, or transient ischemic attack in the family or personal history
- Infection with COVID-19
Other factors linked to an increased risk of stroke include:
- Age – People above the age of 55 have a higher risk of stroke than those under 55.
- Race – African Americans are more likely than other races to suffer a stroke.
- Men are more likely than women to have a stroke. When women get strokes, they are frequently older, and they are more likely than males to die from them.
- Hormones – Using estrogen-containing birth control pills or hormone therapy raises your risk.
Now that we are aware of the symptoms and causes of stroke, let us find out briefly about the treatment options. Note that some of the best brain surgery centers in Mumbai facilitate the best infrastructure for a successful procedure, including brain tumor surgeries in Mumbai.
Treatment procedures for stroke may be as follows:
Carotid endarterectomy: In this procedure, a small incision is made over the carotid artery, and plaque is removed. The artery is then sutured to restore normal blood flow to the brain.
Intra-arterial thrombolysis: in this procedure, a catheter is inserted in the artery and placed near the clot’s proximity. Fibrinolytic agents are released directly onto the clot to break the clot.
Mechanical thrombectomy: A catheter is inserted through the artery to reach the clot. A stent remover is then inserted through the catheter to remove the clot physically.
Carotid angioplasty: The surgeon inserts a catheter in the artery through a sheath. The artery is then injected with contrast material. The contrast material enables a complete view of the artery and its narrower paths. A filter is placed on the other side of the narrowed artery path to catch any debris that breakaway during the procedure.
A balloon is then inserted through the catheter and inflated to broaden the artery path and get the blood flowing. A mesh-like stent is then inserted through the catheter to prevent the arterial walls from collapsing.
Once we treat the patient with a suitable procedure, the patient undergoes stroke rehabilitation, which may include physiotherapy, speech therapy, stimulation therapy, and medication. The time taken for the patient to recover the reduced abilities depends on the extent of damage caused by the stroke.
Remember to act Face Arms Speech Time. After all, awareness and time are the keys to saving a life.
