Migraine Headache Treatment in Mumbai
Migraines are a type of headache with signs and symptoms of sensitivity to light, sounds or smells, eye pain, nausea, and vomiting. If you have a migraine consider visiting Dr. Gurneet Sawhney, an expert neurosurgeon in Mumbai.
Causes of Migraine
The exact mechanism by which migraine pain happens is unknown. The present theory is that it is a disorder of nerves and blood vessels in the brain. Migraine headache attacks might be activated by dietary, hormonal, emotional, physical, and even environmental influences.
Symptoms of Migraine
The main symptom of a migraine is generally a headache followed by severe pain that gets intense with movement and is disabling, that is, prevents an individual from executing normal activities.
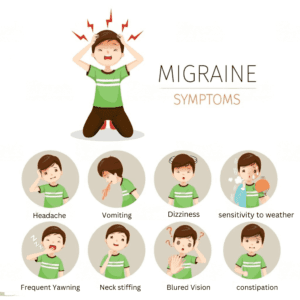
- Early signs: Slight changes one or two days prior to a migraine that directs a migraine might be coming, together with constipation, yawning, mood changes, food hunger, and neck stiffness.
- Aura: Some individuals experience aura before or through the headache. Aura symptoms, that develop over 5 minutes and last for up to 1 hour, might comprise Visual disturbances, such as sparks of light, zig-zag patterns, or blind spots; numbness or stinging on one side of the face or in an arm/ leg section; and feeling quite giddy or off balance.
- Headache: This phase could last from 2 to 72 hours and is observed by a moderate to extreme headache that is excruciating or pulsing, and generally only on one side of the head. An individual may also be more vulnerable to light, sounds, odors, and touch; and undergo sudden chills and sweating, nausea and vomiting, blurry vision, and light-headedness.
- Hangover: Post-migraine attack, an individual may feel exhausted and washed out. Confusion, irritability, dizziness, weakness, and sensitivity to light and sound might also be felt the following day.
Book An Appointment. Contact us now!
Treatment of Migraine Headache
Unfortunately, there is no cure for migraine headaches – the goal of the migraine treatment is to dismiss the symptoms once they start and try to evade further attacks. More than one chronic migraine treatment might help and it may take time for migraine specialists to see what treatments work best. This will include trying various types or blends of medicines.
1 . Pain-relievers

2. Triptans
These are known as prescription drugs developed precisely for migraine headaches. It is believed that triptans work to relieve pain and migraine management by blocking pain pathways and tightening blood vessels in the brain. Some individuals find it effective to combine a triptan with a pain-reliever.
3. Anti-emetics
Anti-sickness medicines, also known as anti-emetics, can decrease the vomiting and nausea related with a migraine headache. They might even be helpful in people who don’t experience nausea or vomiting during their migraine attack. Anti-emetics are best prescription medications and are typically taken along with pain-relievers and triptans.
4. Preventative medicines
Preventative medicines may be prescribed by migraine specialists to decrease the severity or frequency of migraines. They are used when other medicines don’t work; when migraines are severe, continuous or frequent; and when evading possible triggers has not helped to stop migraine pain attacks.
These include various instant migraine relief medications that were originally developed and used to avert seizures in people with epilepsy, manage angina and high blood pressure, and antidepressants.
How is migraine diagnosed?
A chronic migraine usually occurs at least 15 days a month and can result in a poor quality of life and considerable productivity loss. It is necessary to seek treatment for it.
During the consultation, Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawhney will discuss your health history and symptoms so that he can assess your condition.
He may also ask you to undergo a few tests, including blood tests, MRI or CT scans,and electroencephalogram (EEG).
Schedule a consultation today and take the first step to a pain-free life!
 Ways to prevent migraine
Ways to prevent migraine
Following these steps may prevent symptoms:
- Avoid triggers. To do so, maintain a diary to keep track of the symptom patterns so that you can identify them.
- Managing stress helps – practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises.
- Exercise regularly
- Eat on time, and avoid skipping meals.
- Stay hydrated
- Get plenty of rest
You should visit the doctor immediately if
- The headaches are severe and abrupt
- Problems such as a change in vision, trouble with balance and walking, and weakness in a body part or numbness do not get better after the headache goes away
- You have a stiff neck or fever
- The headaches are more severe or different than your regular headache pattern
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a migraine last?
Generally, a migraine headache may last from several hours up to a few days.
Do children get a migraine, and how are they treated?
Yes, even children can suffer from migraines. The treatment for them is similar to adults’ treatment, but the medicine dosage has to be adjusted to suit their age.
What is the difference between acute and preventative migraine therapy?
Acute migraine therapy helps relieve symptoms after the migraine starts, whereas preventative migraine therapy is usually taken to reduce the headaches’ severity, duration, and frequency.
Are migraines dangerous?
Most migraines are not dangerous. However, in extremely rare cases, hemiplegic migraine can sometimes lead to serious complications or coma.
Blogs
Can Neurological Problems Exist With Normal Scans? | Dr. Gurneet Sawhney
Yes—neurological problems can exist even when your MRI or CT scan looks perfectly normal. A clean scan means there's no visible structural damage. It doesn't mean your nervous system is working the way it should. Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawhney, a leading neurosurgeon in...
Is Dementia a Hereditary?|Neurosurgeon in Mumbai.
Dementia does not necessarily occur genetically, but in some people, it can be more likely due to genetics. The majority of the cases related to dementia, such as those related to Alzheimer's disease, are as a result of aging, lifestyle habits, vascular conditions,...
5 Tips for Instant Migraine Relief
Migraines are intense and often debilitating headaches that can disrupt daily life. While medication is one way to manage a migraine, there are several practical, evidence-based strategies you can use for fast relief. As a neurosurgeon, I have seen many patients who...

 Ways to prevent migraine
Ways to prevent migraine

