Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawhney is one of the best neurosurgeons in Mumbai who offers trigeminal neuralgia treatment. As we all know, Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) is an extremely chronic condition that causes pain at the slightest motion or action. Simple actions such as chewing, talking, shaving, or even feeling the wind are likely to cause pain and discomfort in the patient.
So taking it further, Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawhney explains how to distinguish between dental pain and trigeminal neuralgia and its scope of treatment.
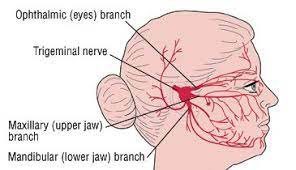
The reason for the facial pain and discomfort is that Trigeminal Neuralgia affects the 5th cranial nerve, also known as trigeminal, one of the most widespread nerves located in the head. Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) is also known as the suicide disease or Tic Douloureux.
Symptoms associated with pain-related with Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) are
- Short and severe stabs of pain usually on one side of the face which last for a couple of seconds to minutes
- Sharp, stabbing pain, electric shock type of pain usually on one side of the face
- Pain is located in the upper, middle, or lower part of the face.
- The patient does not wake up from sleep complaining of pain.
- Pain-associated episodes are of varying duration – continuous or sporadic. There have been instance when pain has lasted for months and vanished or resurged after a couple of months or years.
Distinct characteristics of dental pain
- Dental pain is monotonous, and it is experienced even when chewing.
- Dental pain is characterized by both sensitivities, viz. hot as well as cold.
- The patient can complain of bleeding or discharge and swelling around the tooth, gums, and jaws.
- The pain could be a result of injury or trauma to that area.
The link between trigeminal neuralgia and tooth pain
Trigeminal neuralgia means dysfunctioning of the nervous system, especially the trigeminal nerve, which sends signals to your brain and assists in changes in temperature, touch recognition, and so on. The trigeminal nerve damage could be due to the pressure exerted on it by the surrounding vessels. An irritated trigeminal nerve is likely to make the patient experience short-lasting pain attacks in the facial area.
A patient is at high risk for trigeminal neuralgia if
- Age is above 50 years old
- Suffering from multiple sclerosis or any other nerve-damaging disorder
When should you consult a doctor for facial pain?
It is essential to seek medical consultation in case of intense facial pain that hampers the quality of life. The neurosurgeon will perform neurological tests to accurately diagnose the condition and offer a comprehensive treatment solution that attempts to relieve the existing pain and prevent pain attacks in the future.
Treatment of dental pain associated with Trigeminal Neuralgia
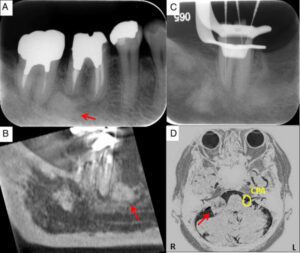
In case of no relief from medications, then the neurosurgeon may suggest minimally invasive surgical procedures to relieve tooth pain associated with trigeminal neuralgia-
Gamma Knife® Radiosurgery for Trigeminal Neuralgia
Gamma Knife® Radiosurgery leads to a reduction in the intensity of pain to a great extent. The healing period could be four to six weeks or a couple of months for best outcomes. Along with gamma knife treatment, the patient needs to consume the prescribed medicines recommended by the neurosurgeon.
The Gamma Knife® Radiosurgery is an outpatient procedure that does not require anesthesia.
Microvascular Decompression for Trigeminal Neuralgia
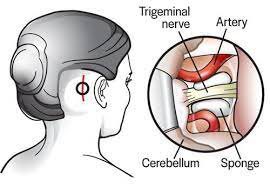
A Microvascular decompression surgery does not harm the trigeminal nerve, while its results are as good as up to 80% in terms of pain relief. However, the patient needs to stay in the hospital for two days, while it could take up to six weeks to return to normal routines.
Dr. Gurneet Singh Sawhney treats trigeminal neuralgia patients at his Neurosurgery clinic in Mumbai.