Acute symptomatic seizures (ASS) occur in close relation to an acute brain injury. Unlike other types of seizures, they’re directly tied to an immediate cause. They often resolve once the doctor understands and treats the cause. It is a distinct type of seizure, essential to recognize for proper management and treatment.
In simple terms, acute symptomatic seizures are like surprise guests at a party. They show up unexpectedly and can cause quite a stir. Imagine your brain throwing a party. Then suddenly, due to an immediate cause like an infection, or head injury, it goes into overdrive.
Now, how often does this happen? Well, about 40% of all first-time seizures are acute symptomatic. That’s a significant number!
When facing such an overwhelming situation, you want the most experienced doctor on your team, right? Enter Dr. Gurneet Sawhney.
Dr. Sawhney is known to many as the best neurosurgeon in Mumbai. He’s not just a neurosurgeon; he’s a maestro in managing these tricky brain episodes. With him, you’re not just getting treatment; you’re getting a roadmap to better brain health.
But wait, how do you know if you’re having an acute symptomatic seizure? Let’s dive into their symptoms next.
Acute Symptomatic Seizure – Symptoms

Understanding the acute symptomatic seizure symptoms is crucial for timely intervention. Here are some critical symptoms highlighted by Dr. Gurneet Sawhney:
- Sudden Loss of Consciousness: The individual may blackout, unable to respond to their surroundings.
- Uncontrollable Muscle Spasms: Limbs might jerk rapidly and rhythmically without any control.
- Confusion: After the seizure, they might feel confused or have trouble understanding where they are.
- Temporary Memory Issues: Difficulty remembering events right before or after the seizure is typical.
- Sensory Disturbances: They might experience unusual smells, sounds, or visual changes.
- Involuntary Movements: This can include twitching, nodding, or even lip-smacking.
Are you or a loved one experiencing these symptoms? Remember, Dr. Sawhney, a leading neurosurgeon in India, is just a call away.
So, what exactly triggers these acute symptomatic seizures? Let’s shed light on the common causes behind these seizures.
Acute Symptomatic Seizure – Causes
“Acute symptomatic seizures don’t just happen out of the blue,” says Dr. Gurneet Sawhney. “They have specific triggers. Essentially, they directly respond to something acutely disturbing the brain’s function.”
Common acute symptomatic seizure causes include:
Head Trauma:
Severe head injuries can harm brain tissue and change brain activity.
Brain Infections:
Conditions like meningitis or encephalitis can cause brain inflammation and affect normal brain function.
Stroke:
A stroke from a blockage or bleeding in the brain can lead to unusual electrical activity.
Brain Tumors:
Brain tumors can press on or damage surrounding tissues. This pressure or injury can disrupt the electrical balance in the brain and cause seizures.
Metabolic Imbalances:
Imbalances in essential substances like blood sugar, sodium, or calcium can provoke seizures. These imbalances affect the brain’s electrical activity and ability to function correctly.
Toxic Substances:
Exposure to certain toxins, including alcohol withdrawal, can lead to ASS. These substances can interfere with the brain’s normal functioning, leading to seizure activity.
Would you like to know more about the potential triggers of ASS? Please contact the distinguished neurosurgeon in Navi Mumbai, Dr. Gurneet Sawhney.
Knowing the causes is just the beginning. How are acute symptomatic seizures diagnosed? Let’s delve into the diagnostic process next.
Acute Symptomatic Seizure – Diagnosis
Acute Symptomatic Seizures require prompt and accurate diagnosis to ensure effective management. The methods that Dr. Gurneet Sawhney, a noted neurosurgeon in Thane, uses include:
- Medical History Review: The doctor begins by meticulously reviewing the patient’s medical history. The primary focus is on potential seizure triggers and pre-existing conditions.
- Neurological Examination: A comprehensive neurological exam assesses brain and nervous system functions. This helps to pinpoint any neurological
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): An EEG records the brain’s electrical activity. It offers critical insights into abnormal patterns that may indicate seizures.
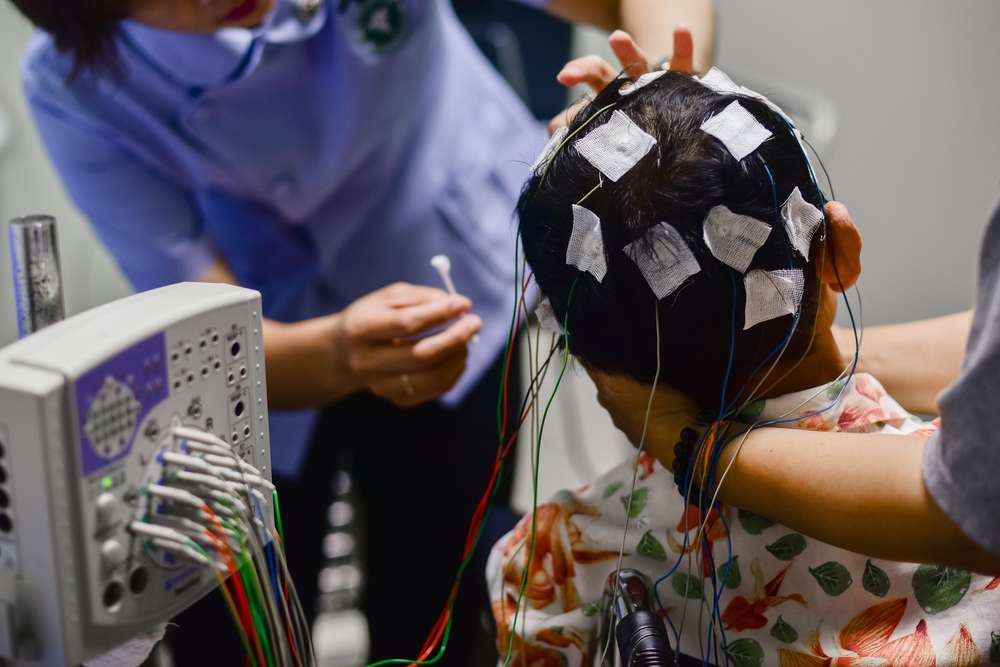

- Brain Imaging: Technologies like MRI or CT scans provide detailed images of the brain. These images aid in the identification of structural causes of seizures.
- Blood Tests: These tests check for underlying health issues like electrolyte imbalances or infections that might trigger seizures.
- Lumbar Puncture: Sometimes, the surgeon may conduct a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) to analyze cerebrospinal fluid. This is to look for signs of infection or inflammation that could lead to seizures.
- Toxicology Screening: This helps detect drugs or toxins that might be responsible for seizure activity. Remember, timely diagnosis is crucial in managing acute symptomatic seizures effectively.
Now, let’s shift gears and explore the recurrent acute symptomatic seizure treatment options.
Treatment Options for Recurrent Acute Symptomatic Seizures (ASS)

Dr. Gurneet Sawhney, an expert in neurological treatment, recommends a multifaceted approach to managing recurrent ASS. The strategies include:
Antiepileptic Drugs (AEDs):
Antiepileptic medications like Levetiracetam or Phenytoin often effectively control seizure frequency and intensity.
Adjusting Medication:
If seizures are due to infections or metabolic imbalances, modifying or introducing medications can be crucial.
Lifestyle Changes:
Patients should adopt a healthy lifestyle, including adequate sleep and stress management. Positive lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce seizure occurrences.
Regular Monitoring:
Continuous monitoring and follow-ups to adjust treatment plans can help ensure optimal seizure control.
Now, let’s explore the circumstances under which long-term treatment becomes a necessity for managing acute symptomatic seizures.
Long-term treatment becomes necessary when:
- A patient experiences repeated seizures
- A patient has underlying conditions like brain injuries or chronic infections
- If initial interventions don’t control seizures
Would you like more information on the management of seizures? Please consult Dr. Gurneet Sawhney, a go-to specialist for seizure treatment in Mumbai.
So, why is it critical to effectively manage acute symptomatic seizures? Continue reading to understand the long-term risks associated with ASS and their preventive strategies.
Long-Term Risks Associated with Acute Symptomatic Seizures
Acute Symptomatic Seizures, if not appropriately managed, can lead to several long-term risks. Notable among these are:
Recurrent Seizures:
There’s a risk of developing recurrent, possibly more severe seizures.
Brain Damage:
Prolonged or repeated seizures can lead to cumulative brain damage. This will affect cognitive and motor functions.
Psychological Impact:
Chronic seizures often have a psychological toll. It can lead to depression or anxiety.
Status Epilepticus:
The seizures last for an extended period or occur back to back without recovery in between. This is a life-threatening condition.
Preventative Strategies
Preventing ASS involves a proactive approach. Key strategies include:
- Regular medical check-ups for early detection of potential triggers or underlying conditions.
- Strict adherence to prescribed antiepileptic drugs.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including adequate sleep, stress management, and avoiding seizure triggers.
- Educating family members and caregivers about seizure management and emergency protocols.
Now, let’s address an important question: Can these seizures be mistaken for other conditions? How does this impact diagnosis and treatment?
Conditions Acute Symptomatic Seizures Can Be Mistaken For
ASS can sometimes be mistaken for other medical conditions. Such cases of misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment.

This misdiagnosis often occurs due to similarities in symptoms with:
- Migraines: Migraines can cause aura-like symptoms, sometimes confused with seizure auras.
- Psychogenic Non-epileptic Seizures (PNES): These are seizure-like episodes caused by psychological factors. They are not electrical disruptions in the brain.
- Syncope (Fainting): Syncope is caused by a temporary drop in blood flow to the brain. It can mimic seizure-induced loss of consciousness.
Are you or a loved one dealing with symptoms that might indicate ASS? Don’t hesitate to get help. Consulting neurology specialists like Dr. Gurneet Sawhney is critical in navigating these challenges. Contact Dr. Sawhney for expert advice and tailored treatment options.
Conclusion
Acute Symptomatic Seizures is a critical neurological condition that demands prompt attention. Managing acute symptomatic seizures requires a thorough understanding of their:
- Accurate diagnosis
- Potential risks
- Prevention strategies
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms suggestive of seizures, please seek professional guidance.
Are you or a loved one struggling with neurological concerns? Don’t navigate the complexities of your health alone.
Reach out to Dr. Gurneet Sawhney, the seasoned neurological expert. Take the first step towards a healthier, happier life. His expertise in accurately diagnosing and treating seizures can significantly impact patient outcomes.
Now, let’s address some frequently asked questions that further clarify Acute Symptomatic Seizures.
FAQ
Q. How long is the treatment for acute symptomatic seizures?
A. The treatment duration varies depending on the underlying cause and the patient’s response to therapy. It can range from a few weeks to several months.
Q. What is the first-line treatment for acute seizures?
A. The first-line treatment for acute seizures typically involves antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). The choice of medication depends on the type of seizure and the individual patient’s needs.
Q. Are there any specific environmental factors that can trigger ASS?
A. Yes, particular triggers can provoke acute symptomatic seizures in susceptible individuals. These include flashing lights
- Lack of sleep
- Extreme stress
- Certain medications like corticosteroids, antipsychotic drugs, antibiotics (penicillin and fluoroquinolones)
Q. Is it possible to fully recover from acute symptomatic seizures?
A. Full recovery from ASS is possible, mainly if reversible conditions cause them. However, the prognosis varies based on the underlying cause and the effectiveness of the treatment.
Q. How does age affect the treatment and management of ASS?
A. Age can significantly impact the treatment approach. For instance, children and older adults may require different medications and dosages. They might also respond differently to treatments compared to other age groups.
